Table of contents
No headings in the article.
I am thrilled to announce that on the 23rd of March 2023 I was invited to attend the Empower Her Technical Bootcamp 3.0 (Cloud Engineering track).
This for me, is an incredible opportunity to learn from industry leaders and experts in the field, and I am honored to have been selected for this program. Throughout the boot camp, I will be immersed in a variety of workshops and training sessions (according to our released curriculum) designed to enhance my skills and knowledge. I look forward to sharing my experiences with you as I embark on this exciting journey of personal and professional growth. Join me as I take on this challenge and discover new ways to empower myself and those around me.
The onboarding session for the Empower Her Bootcamp was an exciting and informative experience. We were introduced to the trainers and facilitators who would be guiding us through the program, and we got a glimpse of what we could expect over the next several weeks. We were also given a comprehensive overview of the schedule, expectations, and requirements for the program.
As part of the Empower Her Bootcamp, we are going to be paired with a group of "accountability sisters." This is a concept that encourages participants to form a bond with each other and to support one another throughout the program. We are accountable to each other for our progress and growth and hold each other to a high standard. This approach is designed to help us stay focused, motivated, and committed to our goals. It's been an incredible experience so far, and I feel fortunate to have such a supportive group of women by my side.

We started with an introduction to the fundamentals of cloud engineering. I learned that Cloud engineering is the practice of designing, building, and maintaining cloud-based systems and applications. Cloud engineering involves a wide range of skills and technologies, including cloud computing, network architecture, security, and automation.
Cloud engineers work with public, private, and hybrid cloud environments to develop scalable and resilient cloud-based solutions that meet the needs of businesses and organizations. They are responsible for designing and implementing cloud infrastructure, deploying and configuring cloud services, monitoring and optimizing cloud performance, and ensuring the security and reliability of cloud-based systems.
Cloud engineering has become increasingly important as more organizations move their applications and data to the cloud. Cloud engineers play a critical role in enabling businesses to take advantage of the benefits of cloud computing, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility.
We learned about the different types of cloud computing. we explored the following:
Public Cloud: This type of cloud computing is accessible to the public via the internet. A third-party cloud service provider owns and operates the infrastructure and resources.
Private Cloud: A private cloud is owned and operated by an organization and is used exclusively by that organization. It is not accessible to the public and can be located on-premise or in a third-party data center.
Hybrid Cloud: As the name suggests, a hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private cloud. Organizations can use public cloud resources for non-sensitive operations while keeping their sensitive data and operations in a private cloud.
In my own research, I learnt of a multi-cloud system of computing. Multi-cloud is a cloud computing strategy that involves using more than one cloud service provider to meet an organization's computing needs. Instead of relying on a single cloud provider for all their IT needs, multi-cloud users may use a combination of public, private, and hybrid clouds from different providers.
The main advantage of multi-cloud is that it allows organizations to avoid vendor lock-in and take advantage of the strengths of different cloud providers. For example, an organization might use Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its scalable computing needs, Microsoft Azure for its robust security features, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for its machine learning capabilities. This approach also helps to reduce the risk of downtime and data loss since services are distributed across multiple cloud providers.
However, multi-cloud also introduces new challenges such as the need for effective management and orchestration of multiple cloud services, ensuring data consistency across different cloud providers, and dealing with potential compatibility issues. To address these challenges, organizations may use tools such as cloud management platforms (CMPs) and cloud orchestration tools to automate and streamline their multi-cloud operations.
We were made aware of the benefits of cloud computing, and they include the following
Scalability: Cloud services offer you the ability to easily scale your resources up or down as your traffic demands change. This means that you can quickly add more resources during peak traffic times, and then scale back down during quieter periods.
Cost savings: Cloud services are typically more cost-effective than traditional hosting solutions, as you only pay for the resources you use. This can help you save money on hosting fees, while still maintaining a high level of performance and reliability.
High availability: Cloud services are designed to be highly available, meaning that your blog will be accessible to your readers at all times. This is because cloud providers typically have redundant systems in place to ensure that your blog is always up and running.
Security: Cloud services also provide high levels of security, with advanced encryption and security protocols in place to protect your data from unauthorized access or theft.
Backup and disaster recovery: Cloud services typically offer automatic backups and disaster recovery options, which can help you quickly recover your data in the event of a hardware failure or other disaster.
We also learned about the types of cloud delivery models:
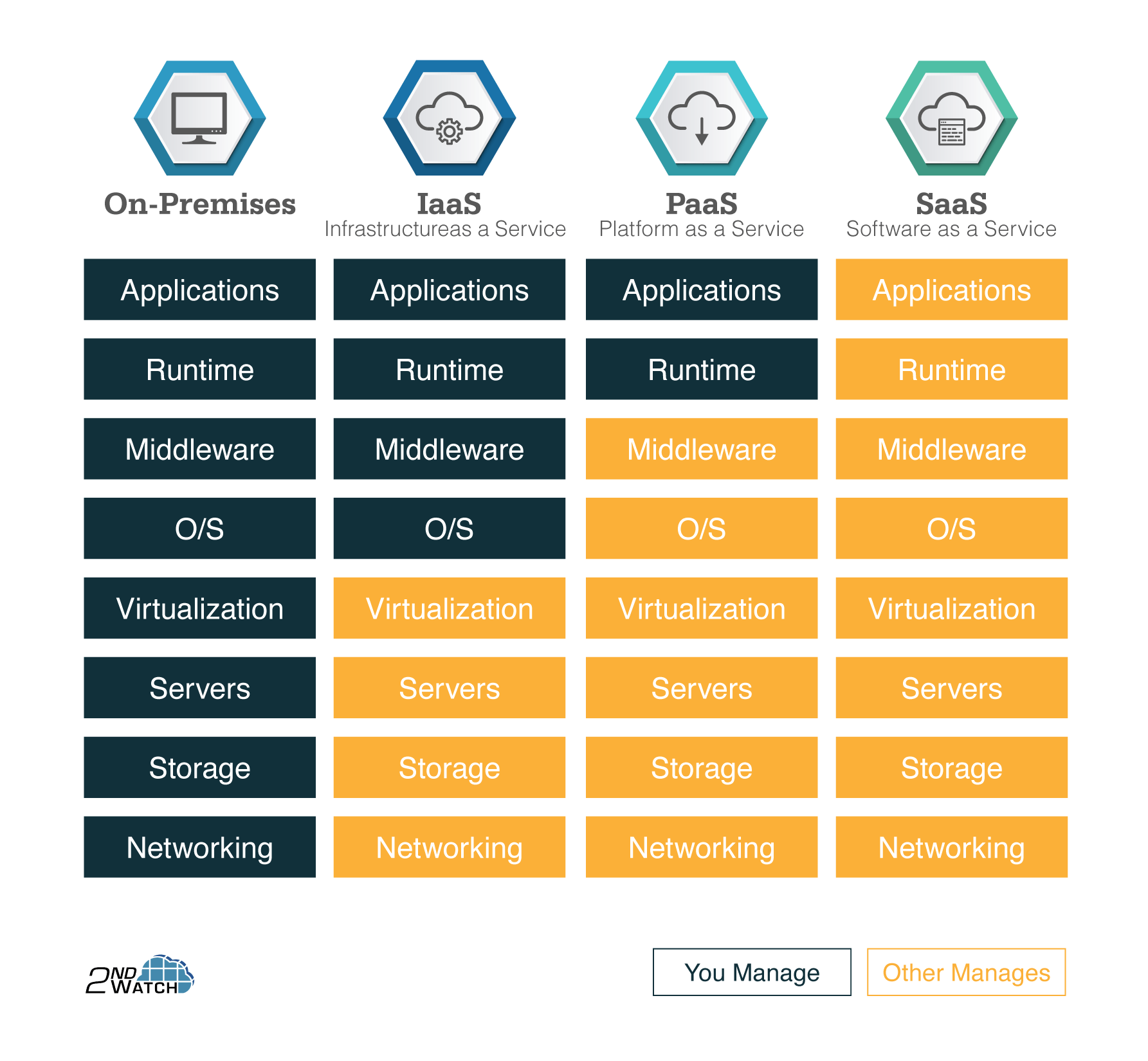
The on-premise cloud model: This is also known as the private cloud model, it is a type of cloud computing infrastructure that is operated and managed by an organization within its own data center or on-premise infrastructure. In this model, the organization maintains complete control over the hardware, software, and security of its cloud computing infrastructure, which is accessed exclusively by its own employees or authorized partners.
The on-premise cloud model is favoured by organizations that require a high level of security, compliance, and control over their data and applications, and are willing to invest in the necessary hardware and software infrastructure to build and maintain their private cloud. This model provides more flexibility and customization options compared to the public cloud, allowing organizations to tailor their cloud infrastructure to meet their specific needs.
However, the on-premise cloud model also requires significant upfront capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance costs, which can be a challenge for small and medium-sized organizations with limited IT budgets. In addition, this model may limit scalability and access to the latest cloud technologies, as organizations are responsible for upgrading and maintaining their infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): In this model, cloud providers offer virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, networking, and operating systems. Users can run their applications and services on top of this infrastructure, allowing them to customize their computing environment.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): In this model, cloud providers offer a platform for developers to build and deploy applications without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure. PaaS providers typically offer tools and services for application development, testing, and deployment, as well as hosting and scaling of the applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS): In this model, cloud providers offer software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. Users can access the software through a web browser or mobile app, without having to install or maintain the software themselves. The provider manages the underlying infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking.
Each of these cloud delivery models offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management for users, depending on their needs and preferences.
Practical Session:
Set up an EC2 instance
Create an IAM user
